每个CPU的实时调度基本数据结构
相关内容的示意图摘自《深入Linux内核架构》
在Linux中遵循POSIX标准实现了两种实时调度算法:FIFO和RR。对于FIFO的使用需要小心,防止出现FIFO独占整个CPU的情况。
调度器基本框架
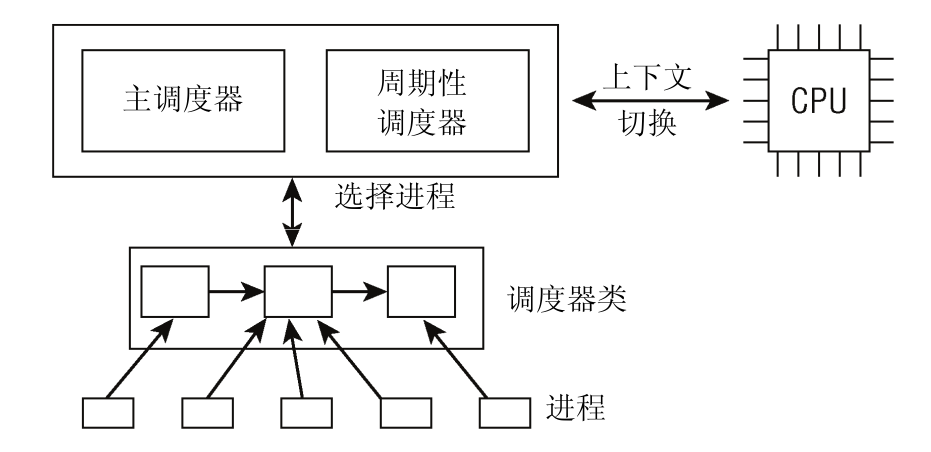
POSIX标准规定的调度算法的声明单位是线程,即假设系统有N个调度算法,那么N个线程最多有N种调度算法。
多种调度算法由一个调度类进行管理,如RR和FIFO都由实时调度类进行管理。该调度类实现内核sched_class结构体要求的所有函数指针的函数实现。
如下图所示即为sched_class的声明: 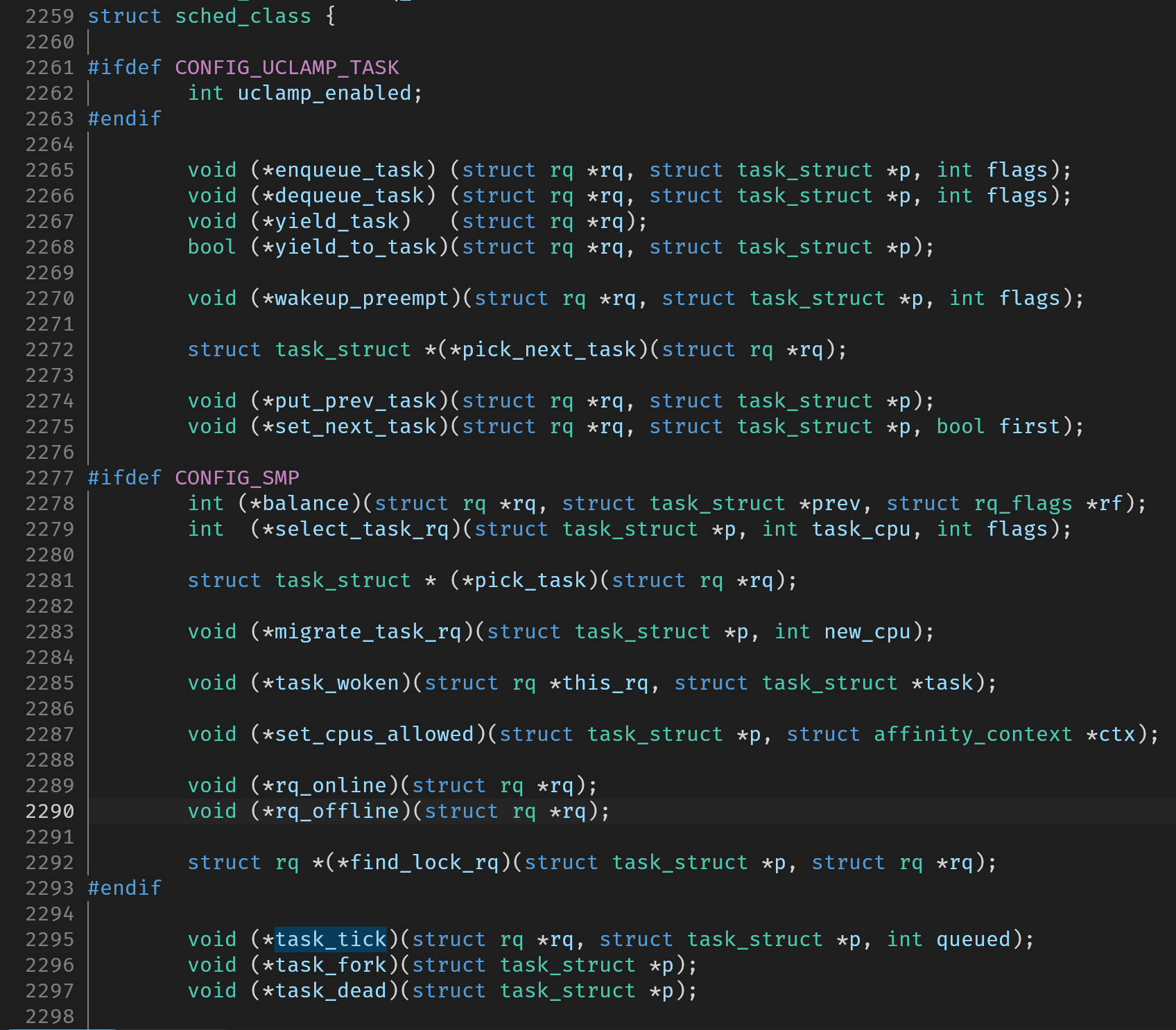
调度类使用了这种方式将实时调度和其他调度区别开来,核心调度器不关心调度类内部实现细节,仅使用sched_class中的函数指针调用对应的函数实现。
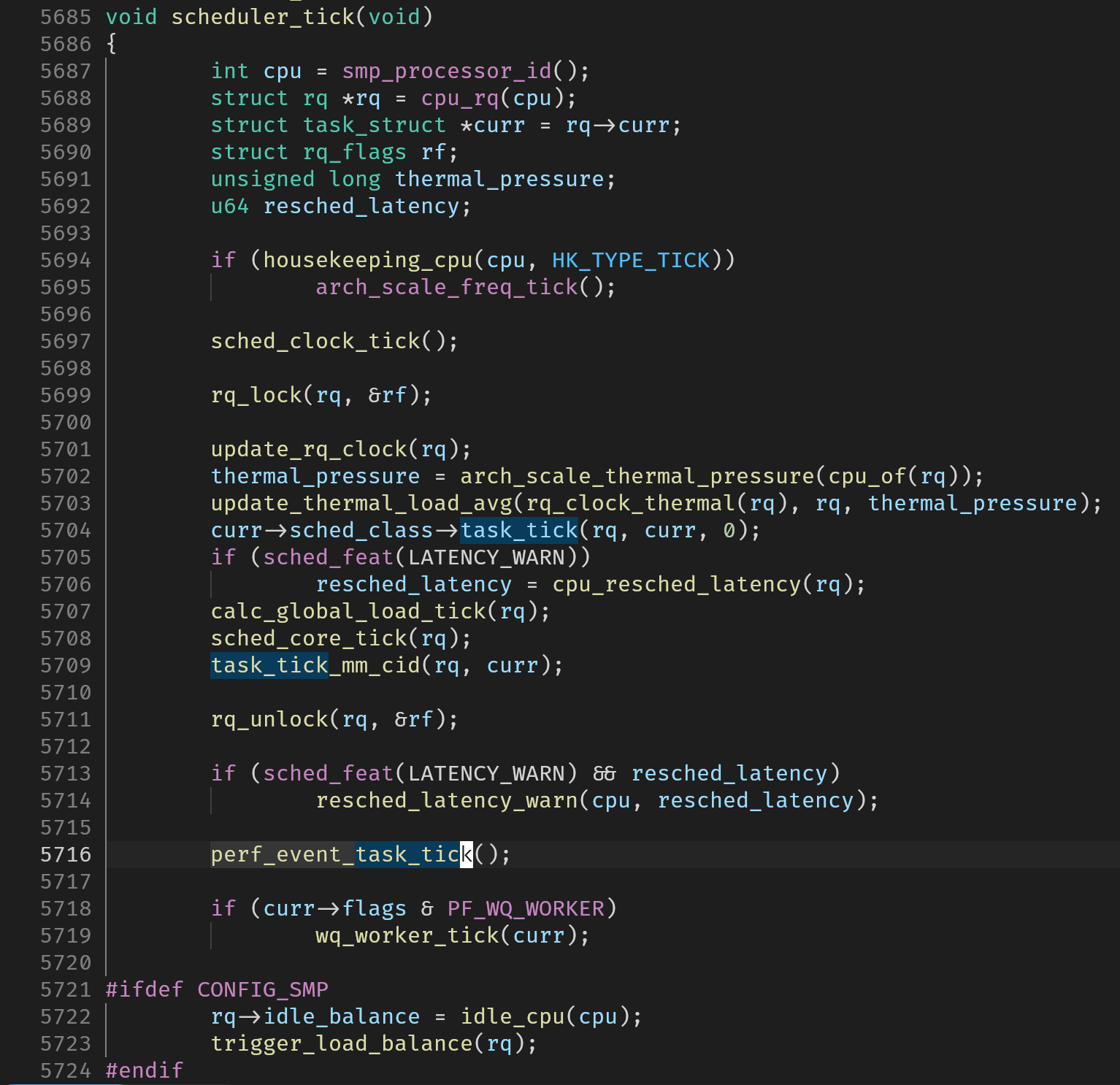
如上图所示,这是核心调度器中的一个tick(1ms)执行一次的处理函数,它中间调用了curr->sched_class->task_tick(...)。对于实时线程,这个函数是由实时调度类(rt_sched_class)提供的task_tick_rt。
rt_sched_class的定义如下: 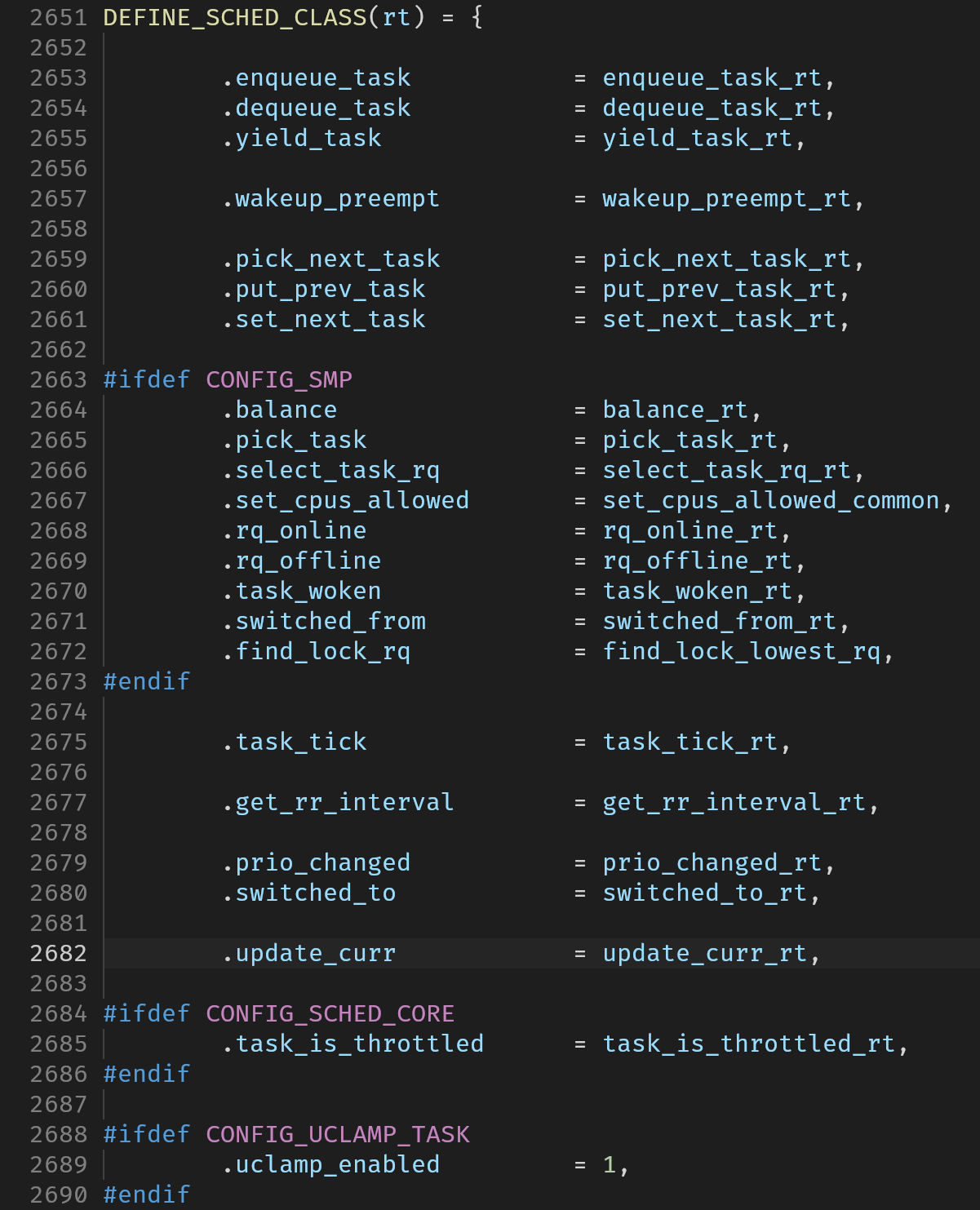
task_struct
struct task_struct {
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
/*
* For reasons of header soup (see current_thread_info()), this
* must be the first element of task_struct.
*/
struct thread_info thread_info;
#endif
unsigned int __state;
/* saved state for "spinlock sleepers" */
unsigned int saved_state;
/*
* This begins the randomizable portion of task_struct. Only
* scheduling-critical items should be added above here.
*/
randomized_struct_fields_start
void *stack;
refcount_t usage;
/* Per task flags (PF_*), defined further below: */
unsigned int flags;
unsigned int ptrace;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
int on_cpu;
struct __call_single_node wake_entry;
unsigned int wakee_flips;
unsigned long wakee_flip_decay_ts;
struct task_struct *last_wakee;
/*
* recent_used_cpu is initially set as the last CPU used by a task
* that wakes affine another task. Waker/wakee relationships can
* push tasks around a CPU where each wakeup moves to the next one.
* Tracking a recently used CPU allows a quick search for a recently
* used CPU that may be idle.
*/
int recent_used_cpu;
int wake_cpu;
#endif
int on_rq;
int prio;
int static_prio;
int normal_prio;
unsigned int rt_priority;
struct sched_entity se;
struct sched_rt_entity rt;
struct sched_dl_entity dl;
struct sched_dl_entity *dl_server;
const struct sched_class *sched_class;
...
pid_t pid;
pid_t tgid;
...
};这是进程调度的结构体,非常长(821行代码),它包含:
- 进程状态和执行信息(PID、优先级、父/子进程指针、待绝信号等)
- 已分配的虚拟内存信息
- 进程身份凭据(用户信息和权限等)
- 使用的程序二进制文件
- 进程处理的文件信息
- 进程间通信有关信息
- 用户定义的信号处理函数
- 调度类的信息(上述
sched_class在task_struct中表现为一个sched_class指针)
等信息
注:task_struct同时用于线程和进程,不只是进程使用,故而调度器也以它为基本单位
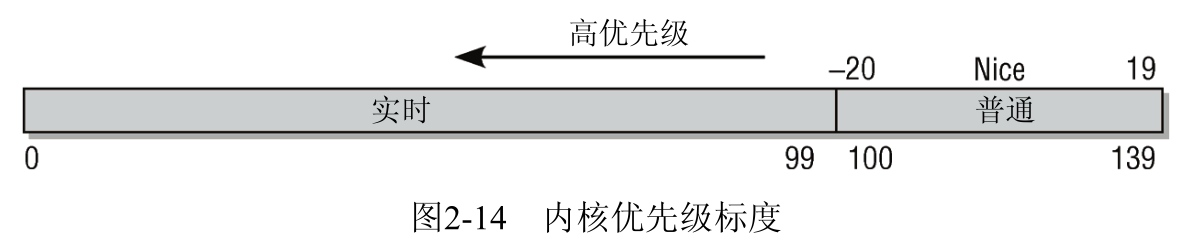
调度优先级prio、static_prio、normal_prio以及rt_priority之间有着微妙的关系,如下图和下表所示:
| 进程类型/优先级 | static_prio | normal_prio | prio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 非实时进程 | static_prio | static_prio | static_prio |
| prio暂时高至实时优先级的非实时进程 | static_prio | static_prio | prio不变 |
| 实时进程 | static_prio | MAX_RT_PRIO-1-rt_priority | prio不变 |
其中,static_prio是通过创建进程时的nice值计算得到的。
__state和saved_state可以表示进程运行的状态,运行状态可以有
- RUNNING(在就绪队列就算,不需要运行)
- INTERRUPTABLE
- UNINTERRUPTIBLE(二者均是睡眠状态)
- STOPPED
- ZOMBIE(僵尸进程是进程已退出却未被父进程调用join回收)
- DEAD
rt_rq结构体
rq是内核设计的一种ready queue结构体
struct rq {
/* runqueue lock: */
raw_spinlock_t __lock;
unsigned int nr_running;
...
struct cfs_rq cfs;
struct rt_rq rt;
struct dl_rq dl;
...
};struct rt_rq {
struct rt_prio_array active;
...
};
struct rt_prio_array {
DECLARE_BITMAP(bitmap, MAX_RT_PRIO+1); /* include 1 bit for delimiter */
struct list_head queue[MAX_RT_PRIO];
};rq中有一个rt_rq的结构体,它完全遵从POSIX规范,其中每个优先级都存储了一个链表,并使用位图存储了哪些优先级有进程(可以加速获取优先级最高的链表的进程)