sandbox是如何实现的?
可能的实现方案:虚拟机(KVM)、软件监狱(container),两者都可用cgroups管理资源配额,而资源隔离的抽象则各自有不同实现(虚拟机虚拟化硬件实现,容器利用namespace抽象隔离系统级别的资源)
pod sandbox是容器的资源隔离工具,在一个pod sandbox中,就共享其中的系统资源
下面以CRI的规范版本v1为例去分析sandbox创建的执行流程
在CRI的定义中,有关于sandbox的API有5个:
service RuntimeService {
rpc RunPodSandbox(RunPodSandboxRequest) returns (RunPodSandboxResponse) {}
rpc StopPodSandbox(StopPodSandboxRequest) returns (StopPodSandboxResponse) {}
rpc RemovePodSandbox(RemovePodSandboxRequest) returns (RemovePodSandboxResponse) {}
rpc PodSandboxStatus(PodSandboxStatusRequest) returns (PodSandboxStatusResponse) {}
rpc ListPodSandbox(ListPodSandboxRequest) returns (ListPodSandboxResponse) {}
// ...
}
message RunPodSandboxRequest {
// Configuration for creating a PodSandbox.
PodSandboxConfig config = 1;
// Named runtime configuration to use for this PodSandbox.
// If the runtime handler is unknown, this request should be rejected. An
// empty string should select the default handler, equivalent to the
// behavior before this feature was added.
// See https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-node/585-runtime-class/README.md
string runtime_handler = 2;
}本质上,维护一个pod sandbox就是在维护一个pod,所以isulad的sandbox模块可以更简单地理解为pod模块
如果去查CRI标准,就会发现没有直接维护Pod的接口,而都是维护PodSandbox的接口
在isulad中,有两种sandbox的控制器:shim和sandboxer
前者利用pause容器的接口将sandbox管理请求转发给executor(如下图所示);后者有单独的sandboxer进程管理底层沙箱逻辑,sandboxer控制器通过gRPC请求实现控制
其中RunPodSandbox就是申请创建一个pod所需要的资源并运行这个pod的过程,将该过程详细分析,就能理解沙箱具体在维护什么
RunPodSandbox
入口通过gRPC定义来实现,客户端以gRPC的方式调用服务
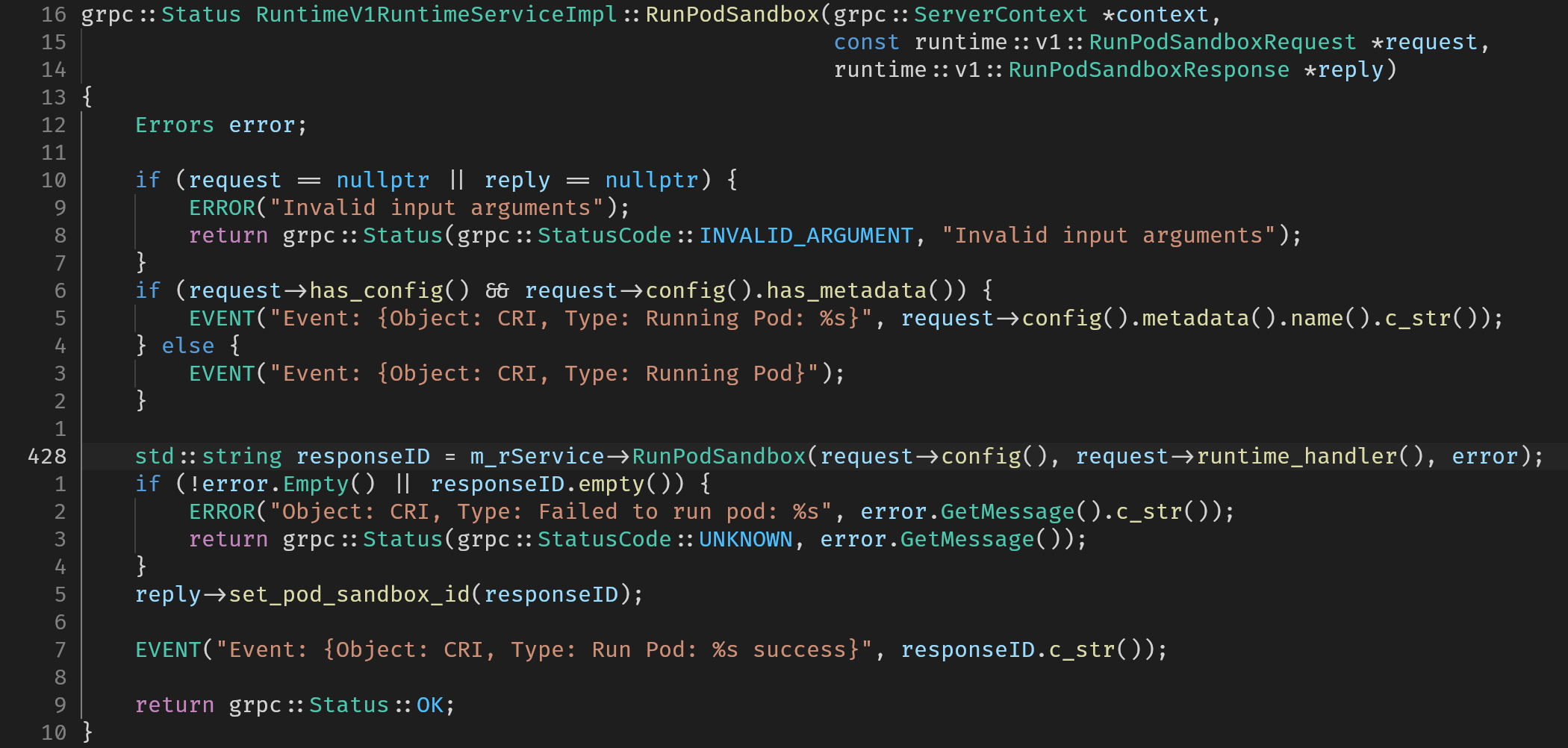
下面将m_rService->RunPodSandbox拆分为如下图右半部分所示的调用过程逐一分析
PrepareSandboxData
将config信息和runtime_handler信息记录到内部变量中
EnsureSandboxImageExists
确保指定的sandbox镜像存在(只有对于sandboxer是shim的情况需要检查)
首先会调用ImageStatus,会在集群中查找该镜像是否存在
如果ImageStatus检查调用的gRPC返回了错误,则需要额外再调用PullImage的gRPC从远端仓库(registry)拉取镜像
注:这里的镜像指的是在沙箱中运行的容器的镜像
PrepareSandboxCheckpoint
该方法将配置文件生成为json格式的checkpoint,其中会有哈希值校验过程,防止出现被篡改的配置
UpdateSandboxConfig
将config中的label、annotation、resources等字段进行更新,设置为默认值,用于在后续调用CreateSandbox时传入作为配置
if namespace_is_cni then PrepareSandboxKey
config中NamespaceMode配置该sandbox是用于pod还是node,前者是通用的k8s的pod(资源管理以pod为单位),后者是在一个主机上运行的抽象(资源管理以主机为单位)
在PrepareSandboxData时会设置networkMode为"cni"或"host",若NamespaceMode为pod则networkMode为"cni",node则networkMode为"host"
config中关于NamespaceMode的proto文件定义:
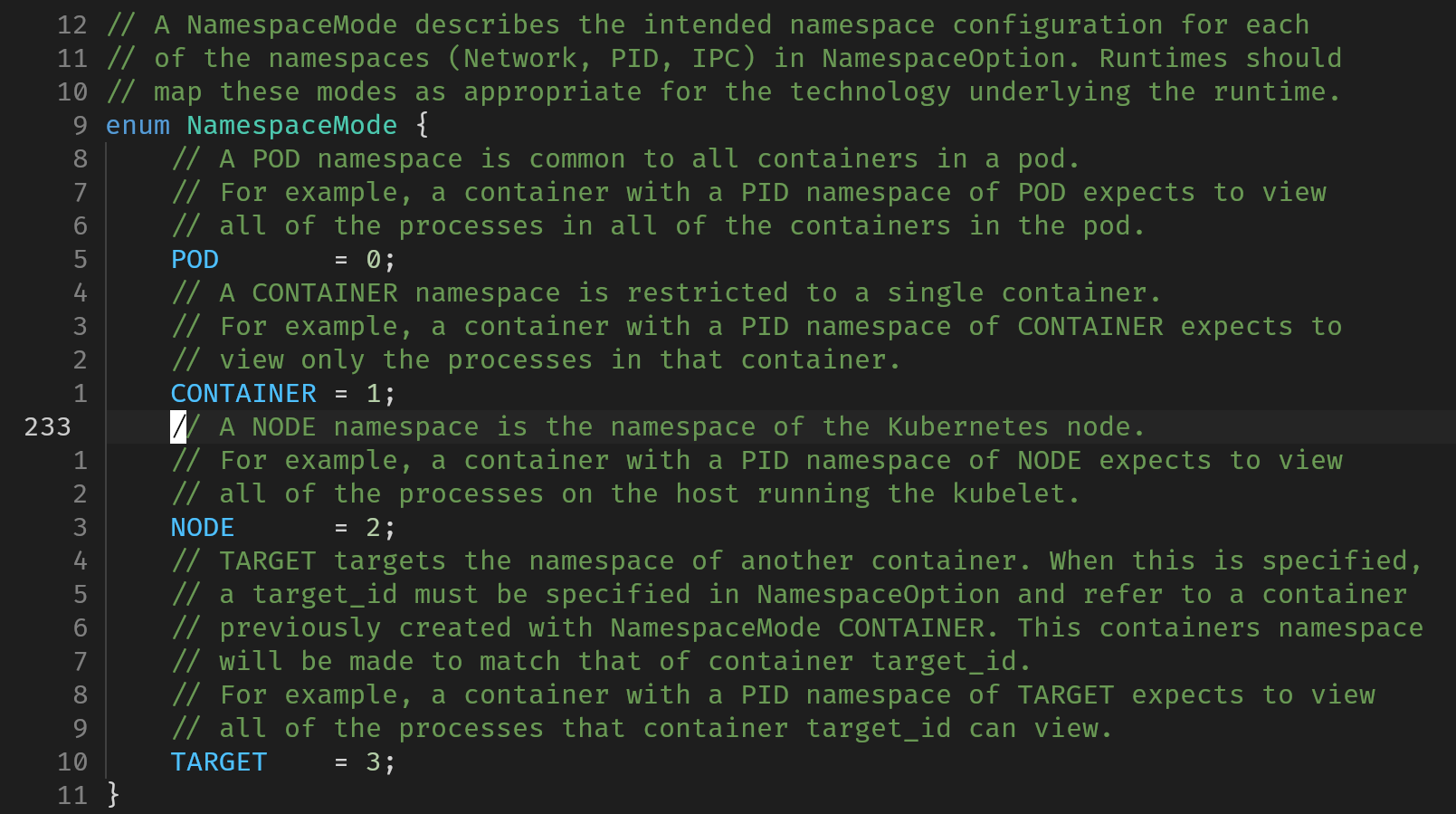
namespace_is_cni检查了当前networkMode是否是"cni",是则执行PrepareSandboxKey,它会通过文件接口创建一个新的network namespace(随机初始化namespace名字,在isulad中被称为network/sandbox key)
SandboxManager::CreateSandbox
先通过util_valid_container_id_or_name检查容器id或名字是否合法(简单使用正则匹配来检查)以及网络设置的检查(若网络模式为"cni",则需要sandbox key非空)
检查完成后利用ControllerManager其实例内存储的sandboxer字符串到Controller的映射找到对应的Controller(本例以shim为例)
检查是否有旧的重名/重id/重前缀的sandbox,有则报错退出
完成后将sandbox的name传入SandboxManager生成对应的id,将二者与该sandbox的映射建立
上述初始化过程完成后,即可创建一个新的Sandbox对象
sandbox = std::shared_ptr<Sandbox>(new Sandbox(id, m_rootdir, m_statedir, name, info, netMode, netNsPath,
sandboxConfig, image));
sandbox->SetController(controller);
/// 创建相关的文件夹
sandbox->PrepareSandboxDirs(error);
/// 将id与sandbox指针/sandbox name的映射保存在Sandbox成员中
SaveSandboxToStore(id, sandbox);SetupSandboxNetwork
void PodSandboxManagerService::SetupSandboxNetwork(const std::shared_ptr<sandbox::Sandbox> sandbox,
std::string &network_settings_json, Errors &error)
{
const auto config = sandbox->GetSandboxConfig();
sandbox->SetNetworkReady(false);
// Setup sandbox files
if (config.has_dns_config() && !sandbox->GetResolvPath().empty()) {
INFO("Overwrite resolv.conf: %s", sandbox->GetResolvPath().c_str());
/// 把config中的网络相关数据写到文件中
SetupSandboxFiles(sandbox->GetResolvPath(), config, error);
if (error.NotEmpty()) {
ERROR("Failed to setup sandbox files");
return;
}
}
if (!namespace_is_cni(sandbox->GetNetMode().c_str())) {
return;
}
const std::string &sandboxKey = sandbox->GetNetNsPath();
if (sandboxKey.empty()) {
error.Errorf("Sandbox key is invalid");
ERROR("Sandbox key is invalid");
return;
}
std::map<std::string, std::string> stdAnnos;
/// 将annotations解析到stdAnnos的map中
CRIHelpers::ProtobufAnnoMapToStd(config.annotations(), stdAnnos);
stdAnnos.insert(std::pair<std::string, std::string>(CRIHelpers::Constants::POD_SANDBOX_KEY, sandboxKey));
std::map<std::string, std::string> networkOptions;
networkOptions["UID"] = config.metadata().uid();
/// 将对应的network namespace的路径挂载
if (prepare_network_namespace(sandboxKey.c_str(), false, 0) != 0) {
error.Errorf("Failed to prepare network namespace: %s", sandboxKey.c_str());
ERROR("Failed to prepare network namespace: %s", sandboxKey.c_str());
return;
}
// Setup networking for the sandbox.
m_pluginManager->SetUpPod(config.metadata().namespace_(), config.metadata().name(),
Network::DEFAULT_NETWORK_INTERFACE_NAME, sandbox->GetId(), stdAnnos, networkOptions,
network_settings_json, error);
if (error.NotEmpty()) {
ERROR("SetupPod failed: %s", error.GetCMessage());
if (remove_network_namespace(sandboxKey.c_str()) != 0) {
ERROR("Failed to remove network namespace: %s", sandboxKey.c_str());
}
return;
}
sandbox->SetNetworkReady(true);
DEBUG("set %s ready", sandbox->GetId().c_str());
}网络插件管理会使用SetupPod创建该pod的网络
sandbox->Save
将sandbox的各种数据保存到硬盘中
分为SaveState、SaveMetadata和SaveNetworkSetting
SaveState完成了状态保存(包括何时创建、何时退出、何时更新、pod id、当前状态),将sandbox的状态生成JSON格式写入文件中
SaveMetadata保存id、Pod名、运行时、sandboxer、网络模式、net namespace的路径等等
SaveNetworkSetting保存网络设置配置信息(字符串形式)
sandbox->Create
会利用Sandbox对象已有的参数,调用Controller类的Create方法创建sandbox,如果是shim则使用ShimController::Create创建(Controller是基类),最终交由isulad的全局executor(g_isulad_service_executor->container.create())以rpc的方式完成sandbox创建
auto Sandbox::Create(Errors &error) -> bool
{
struct ControllerCreateParams params;
// currently, params.mounts is unused.
params.config = m_sandboxConfig;
params.netNSPath = m_netNsPath;
params.sandboxName = m_name;
params.image = m_image;
params.netMode = m_netMode;
params.runtime = GetRuntime();
params.sandboxer = GetSandboxer();
params.hostname = m_sandboxConfig->hostname();
/// ...
if (!m_controller->Create(m_id, params, error)) {
/// ...
return false;
}
return true;
}bool ShimController::Create(const std::string &sandboxId,
const ControllerCreateParams ¶ms,
Errors &error)
{
if (m_cb == nullptr || m_cb->container.create == nullptr) {
ERROR("Unimplemented callback");
error.SetError("Unimplemented callback");
return false;
}
auto requestWrapper = GenerateSandboxCreateContainerRequest(sandboxId, params, error);
if (error.NotEmpty()) {
return false;
}
container_create_response *response {nullptr};
int ret = m_cb->container.create(requestWrapper->get(), &response);
auto responseWrapper = makeUniquePtrCStructWrapper<container_create_response>(response, free_container_create_response);
if (ret != 0) {
if (response != nullptr && (response->errmsg != nullptr)) {
ERROR("Failed to call create container callback: %s", response->errmsg);
error.SetError(response->errmsg);
} else {
ERROR("Failed to call create container callback");
error.SetError("Failed to call create container callback");
}
}
return error.Empty();
}以创建容器的rpc请求创建sandbox,实际上isulad中executor唯一的调用模块就是container,container模块再调用各种运行时(lxc、runc、qemu stratovirt)完成创建
sandbox->UpdateNetworkSettings
将SetupSandboxNetwork中得到的网络设置利用sandbox持久化到硬盘中
sandbox->Start
调用Controller的Start方法,最终会调用ShimController的Start,最终同样调用了executor的接口(g_isulad_service_executor->container.start())完成启动容器